1.3. A Quick Tour¶
1.3.1. Goal¶
This tutorial will expand on the First Run tutorial by taking a quick tour around some of the features of buildbot that are hinted at in the comments in the sample configuration. We will simply change parts of the default configuration and explain the activated features.
As a part of this tutorial, we will make buildbot do a few actual builds.
This section will teach you how to:
- make simple configuration changes and activate them
- deal with configuration errors
- force builds
- enable and control the IRC bot
- enable ssh debugging
- add a 'try' scheduler
1.3.2. Setting Project Name and URL¶
Let's start simple by looking at where you would customize the buildbot's project name and URL.
We continue where we left off in the First Run tutorial.
Open a new terminal, and first enter the same sandbox you created before (where $EDITOR is your editor of choice like vim, gedit, or emacs):
cd
cd tmp/buildbot
source sandbox/bin/activate
$EDITOR master/master.cfg
Now, look for the section marked PROJECT IDENTITY which reads:
####### PROJECT IDENTITY
# the 'title' string will appear at the top of this buildbot installation's
# home pages (linked to the 'titleURL').
c['title'] = "Pyflakes"
c['titleURL'] = "http://divmod.org/trac/wiki/DivmodPyflakes"
If you want, you can change either of these links to anything you want to see what happens when you change them.
After making a change go into the terminal and type:
buildbot reconfig master
You will see a handful of lines of output from the master log, much like this:
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] loading configuration from /home/dustin/tmp/buildbot/master/master.cfg
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] configuration update started
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] builder runtests is unchanged
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] removing IStatusReceiver <WebStatus on port tcp:8010 at 0x2aee368>
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] (TCP Port 8010 Closed)
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] Stopping factory <buildbot.status.web.baseweb.RotateLogSite instance at 0x2e36638>
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] adding IStatusReceiver <WebStatus on port tcp:8010 at 0x2c2d950>
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] RotateLogSite starting on 8010
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] Starting factory <buildbot.status.web.baseweb.RotateLogSite instance at 0x2e36e18>
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] Setting up http.log rotating 10 files of 10000000 bytes each
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] WebStatus using (/home/dustin/tmp/buildbot/master/public_html)
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] removing 0 old schedulers, updating 0, and adding 0
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] adding 1 new changesources, removing 1
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] gitpoller: using workdir '/home/dustin/tmp/buildbot/master/gitpoller-workdir'
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] GitPoller repository already exists
2011-12-04 10:11:09-0600 [-] configuration update complete
Reconfiguration appears to have completed successfully.
The important lines are the ones telling you that it is loading the new configuration at the top, and the one at the bottom saying that the update is complete.
Now, if you go back to the waterfall page, you will see that the project's name is whatever you may have changed it to and when you click on the URL of the project name at the bottom of the page it should take you to the link you put in the configuration.
1.3.3. Configuration Errors¶
It is very common to make a mistake when configuring buildbot, so you might as well see now what happens in that case and what you can do to fix the error.
Open up the config again and introduce a syntax error by removing the first single quote in the two lines you changed, so they read:
c[title'] = "Pyflakes
c[titleURL'] = "http://divmod.org/trac/wiki/DivmodPyflakes"
This creates a Python SyntaxError.
Now go ahead and reconfig the buildmaster:
buildbot reconfig master
This time, the output looks like:
2015-08-14 18:40:46+0000 [-] beginning configuration update
2015-08-14 18:40:46+0000 [-] Loading configuration from '/data/buildbot/master/master.cfg'
2015-08-14 18:40:46+0000 [-] error while parsing config file:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/buildbot/master.py", line 265, in reconfig
d = self.doReconfig()
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/twisted/internet/defer.py", line 1274, in unwindGenerator
return _inlineCallbacks(None, gen, Deferred())
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/twisted/internet/defer.py", line 1128, in _inlineCallbacks
result = g.send(result)
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/buildbot/master.py", line 289, in doReconfig
self.configFileName)
--- <exception caught here> ---
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/buildbot/config.py", line 156, in loadConfig
exec f in localDict
exceptions.SyntaxError: EOL while scanning string literal (master.cfg, line 103)
2015-08-14 18:40:46+0000 [-] error while parsing config file: EOL while scanning string literal (master.cfg, line 103) (traceback in logfile)
2015-08-14 18:40:46+0000 [-] reconfig aborted without making any changes
Reconfiguration failed. Please inspect the master.cfg file for errors,
correct them, then try 'buildbot reconfig' again.
This time, it's clear that there was a mistake in the configuration. Luckily, the Buildbot master will ignore the wrong configuration and keep running with the previous configuration.
The message is clear enough, so open the configuration again, fix the error, and reconfig the master.
1.3.4. Your First Build¶
By now you're probably thinking: "All this time spent and still not done a single build? What was the name of this project again?"
On the waterfall page, click on the runtests link. You'll see a builder page, and in the upper-right corner is a box where you can login. The default username and password are both "pyflakes". Once you've logged in, you will see some new options that allow you to force a build:
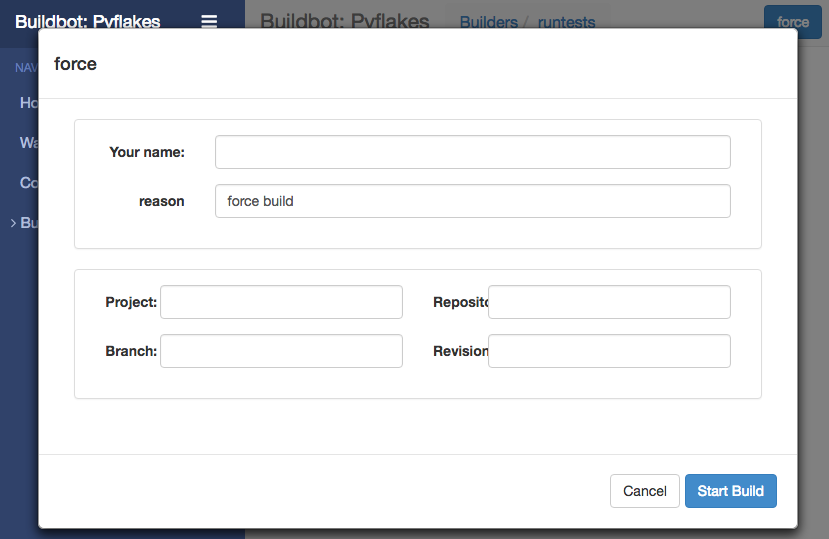
Click Force Build - there's no need to fill in any of the fields in this case. Next, click on view in waterfall.
You will now see:
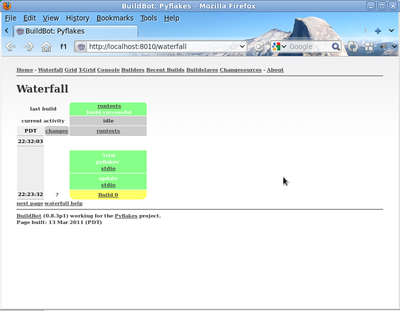
1.3.5. Enabling the IRC Bot¶
Buildbot includes an IRC bot that you can tell to join a channel and control to report on the status of buildbot.
First, start an IRC client of your choice, connect to irc.freenode.org and join an empty channel.
In this example we will use #buildbot-test, so go join that channel.
(Note: please do not join the main buildbot channel!)
Edit :file:'master.cfg' and look for the STATUS TARGETS section. At the end of that section add the lines:
from buildbot.status import irc
c['status'].append(irc.IRC(host="irc.freenode.org", nick="bbtest",
channels=["#buildbot-test"]))
Reconfigure the build master then do:
grep -i irc master/twistd.log
The log output should contain a line like this:
2015-08-14 20:00:33+0000 [-] Starting factory <buildbot.status.words.IrcStatusFactory instance at 0x7fee15c640e0>
2015-08-14 20:00:48+0000 [IrcStatusBot,client] <buildbot.status.words.IrcStatusBot instance at 0x7fee1653f1b8>: I have joined #buildbot-test
You should see the bot now joining in your IRC client. In your IRC channel, type:
bbtest: commands
to get a list of the commands the bot supports.
Let's tell the bot to notify certain events, to learn which EVENTS we can notify on:
bbtest: help notify
Now let's set some event notifications:
bbtest: notify on started
bbtest: notify on finished
bbtest: notify on failure
The bot should have responded to each of the commands:
<@lsblakk> bbtest: notify on started
<bbtest> The following events are being notified: ['started']
<@lsblakk> bbtest: notify on finished
<bbtest> The following events are being notified: ['started', 'finished']
<@lsblakk> bbtest: notify on failure
<bbtest> The following events are being notified: ['started', 'failure', 'finished']
Now, go back to the web interface and force another build.
Notice how the bot tells you about the start and finish of this build:
< bbtest> build #1 of runtests started, including []
< bbtest> build #1 of runtests is complete: Success [build successful] Build details are at http://localhost:8010/builders/runtests/builds/1
You can also use the bot to force a build:
bbtest: force build runtests test build
But to allow this, you'll need to have allowForce in the IRC configuration:
c['status'].append(irc.IRC(host="irc.freenode.org", nick="bbtest",
allowForce=True,
channels=["#buildbot-test"]))
This time, the bot is giving you more output, as it's specifically responding to your direct request to force a build, and explicitly tells you when the build finishes:
<@lsblakk> bbtest: force build runtests test build
< bbtest> build #2 of runtests started, including []
< bbtest> build forced [ETA 0 seconds]
< bbtest> I'll give a shout when the build finishes
< bbtest> build #2 of runtests is complete: Success [build successful] Build details are at http://localhost:8010/builders/runtests/builds/2
You can also see the new builds in the web interface.
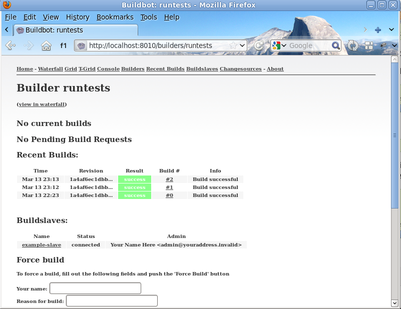
1.3.6. Setting Authorized Web Users¶
Further down, look for the WebStatus configuration:
c['status'] = []
from buildbot.status import html
from buildbot.status.web import authz, auth
authz_cfg=authz.Authz(
# change any of these to True to enable; see the manual for more
# options
auth=auth.BasicAuth([("pyflakes","pyflakes")]),
gracefulShutdown = False,
forceBuild = 'auth', # use this to test your worker once it is set up
forceAllBuilds = False,
pingBuilder = False,
stopBuild = False,
stopAllBuilds = False,
cancelPendingBuild = False,
)
c['status'].append(html.WebStatus(http_port=8010, authz=authz_cfg))
The auth.BasicAuth() define authorized users and their passwords.
You can change these or add new ones.
1.3.7. Debugging with Manhole¶
You can do some debugging by using manhole, an interactive Python shell. It exposes full access to the buildmaster's account (including the ability to modify and delete files), so it should not be enabled with a weak or easily guessable password.
To use this you will need to install an additional package or two to your virtualenv:
cd
cd tmp/buildbot
source sandbox/bin/activate
easy_install pycrypto
easy_install pyasn1
In your master.cfg find:
c = BuildmasterConfig = {}
Insert the following to enable debugging mode with manhole:
####### DEBUGGING
from buildbot import manhole
c['manhole'] = manhole.PasswordManhole("tcp:1234:interface=127.0.0.1","admin","passwd")
After restarting the master, you can ssh into the master and get an interactive Python shell:
ssh -p1234 admin@127.0.0.1
# enter passwd at prompt
Note
The pyasn1-0.1.1 release has a bug which results in an exception similar to this on startup:
exceptions.TypeError: argument 2 must be long, not int
If you see this, the temporary solution is to install the previous version of pyasn1:
pip install pyasn1-0.0.13b
If you wanted to check which workers are connected and what builders those workers are assigned to you could do:
>>> master.workers.workers
{'example-worker': <Worker 'example-worker', current builders: runtests>}
Objects can be explored in more depth using dir(x) or the helper function show(x).
1.3.8. Adding a 'try' scheduler¶
Buildbot includes a way for developers to submit patches for testing without committing them to the source code control system. (This is really handy for projects that support several operating systems or architectures.)
To set this up, add the following lines to master.cfg:
from buildbot.scheduler import Try_Userpass
c['schedulers'] = []
c['schedulers'].append(Try_Userpass(
name='try',
builderNames=['runtests'],
port=5555,
userpass=[('sampleuser','samplepass')]))
Then you can submit changes using the try command.
Let's try this out by making a one-line change to pyflakes, say, to make it trace the tree by default:
git clone git://github.com/buildbot/pyflakes.git pyflakes-git
cd pyflakes-git/pyflakes
$EDITOR checker.py
# change "traceTree = False" on line 185 to "traceTree = True"
Then run buildbot's try command as follows:
source ~/tmp/buildbot/sandbox/bin/activate
buildbot try --connect=pb --master=127.0.0.1:5555 --username=sampleuser --passwd=samplepass --vc=git
This will do git diff for you and send the resulting patch to the server for build and test against the latest sources from Git.
Now go back to the waterfall page, click on the runtests link, and scroll down. You should see that another build has been started with your change (and stdout for the tests should be chock-full of parse trees as a result). The "Reason" for the job will be listed as "'try' job", and the blamelist will be empty.
To make yourself show up as the author of the change, use the --who=emailaddr option on buildbot try to pass your email address.
To make a description of the change show up, use the --properties=comment="this is a comment" option on buildbot try.
To use ssh instead of a private username/password database, see Try_Jobdir.
